Strain Data Sheet
RBRC00254
Strain Information | |
|---|---|
| Image | 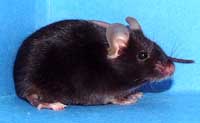 |
| BRC No. | RBRC00254 |
| Type | Transgene Congenic |
| Species | Mus musculus |
| Strain name | B6.Cg-Tg(Camk2a-cre)20Kmik/KmikRbrc |
| Former Common name | C57BL/6-TgN(a-CaMKII-nlCre)/20 |
| H-2 Haplotype | |
| ES Cell line | |
| Background strain | C57BL/6JJcl |
| Appearance | black |
| Strain development | Developed by Futatsugi A. The Cre-Strain series were transfered to Experimental Animal Division, RIKEN Tsukuba Institute in 1999. |
| Strain description | The Cre-recombinase activity was detected specifically in the nuclear fraction of the cerebrum. The expression level of the cre in each line of Tg mice was following order; Line 10, 26> 22, 17N > 17A, 11, 20. The expression of the cre was detected by RT-PCR (including semi-quantitativeone), Western blotting and the Cre-recombinase activity assay. There are some variation in the amount of expression in the cerebrum and leaky expression (less than 1/10 to 1/100 of that in the cerebrum at maximum) in the cerebellum among the different lines. |
| Colony maintenance | Maintained by sister-brother mating. Breed well, Hemizygote x Wild-type, or hemizygote hemizygote. |
| References | |
Health Report | |
|---|---|
| Examination Date / Room / Rack | |
Gene | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gene Symbol | Gene Name | Chr. | Allele Symbol | Allele Name | Common Names | Promoter | Diseases Related to This Gene |
| cre | Phage P1 Cre recombinase | UN | cre | mouse Camk2a promoter | |||
| nls | SV40 large T antigen nuclear localization signal (NLS) | UN | nls | ||||
Phenotype | |
|---|---|
| Annotation by Mammalian phenotyhpe ontology | |
| Detailed phenotype data | |
Ordering Information | |
|---|---|
| Donor DNA | mouse a-CaMKII promoter, Simian virus 40 Large T antigen nuclear localization signal (NLS), phage P1 Cre recombinase DNA, poly A |
| Research application | Cre/loxP system Neurobiology Research Cre driver |
| Specific Term and Conditions | The RECIPIENT of BIOLOGICAL RESOURCE shall prior contact with the DEPOSITOR, discussn use of it and obtain a prior written consent on use of it from the DEPOSITOR. The RECIPIENT agrees to use the BIOLOGICAL RESOURCE only for publication of research papers and NOT for commercial use. The RECIPIENT can use the BIOLOGICAL RESOURCE in a collaboration basis with the DEPOSITOR, except for some cases where only ACKNOLEGEMENT is requested by citing the DEPOSITOR. BEFORE the publication on the BIOLOGICAL RESOURCE by the DEPOSITOR, the RECIPIENT agrees to use the BIOLOGICAL RESOURCE in collaboration with the DEPOSITOR and add Drs. Akira Futatsugi and Katsuhiko Mikoshiba as a co-authors. The RECIPIENT agrees to cite publications requested by the DEPOSITOR. |
| Depositor | Katsuhiko Mikoshiba (RIKEN) |
| Strain Status |  Frozen embryos Frozen embryos Frozen sperm Frozen sperm |
| Strain Availability | Recovered litters from cryopreserved embryos (2 to 4 months) Cryopreserved sperm (within 1 month) Cryopreserved embryos (within 1 month) |
| Additional Info. | Necessary documents for ordering:
Genotyping protocol -PCR- |
BRC mice in Publications |
|---|
Yuki Yoshimura, Tatsuo Watanabe, Kazuomi Nakamura, Akira Futatsugi, Katsuhiko Mikoshiba & Takeshi Y. Hiyama High-temperature exposure during the early embryonic stage lowers core body temperature after growth via a hypothalamic Igfbp2-dependent mechanism Scientific Reports (2024) 39627352 |
Iwano T, Masuda A, Kiyonari H, Enomoto H, Matsuzaki F. Prox1 postmitotically defines dentate gyrus cells by specifying granule cell identity over CA3 pyramidal cell fate in the hippocampus. Development 139(16) 3051-62(2012) 22791897 |
Yabe D, Fukuda H, Aoki M, Yamada S, Takebayashi S, Shinkura R, Yamamoto N, Honjo T. Generation of a conditional knockout allele for mammalian Spen protein Mint/SHARP. Genesis 45(5) 300-6(2007) 17457934 |